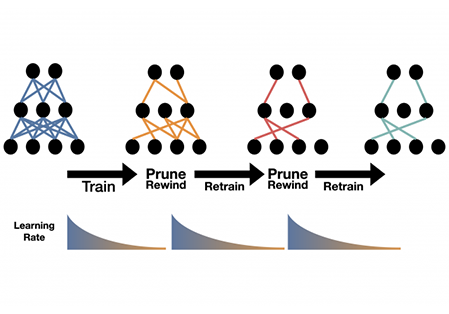
Category
Algorithms & Theory
Language
C++
Ligra is a lightweight framework for processing graphs in shared memory. It is particularly suited for implementing parallel graph traversal algorithms where only a subset of the vertices are processed in an iteration. The project was motivated by the fact that the largest publicly available real-world graphs all fit in shared memory. When graphs fit in shared-memory, processing them using Ligra can give performance improvements of up orders of magnitude compared to distributed-memory graph processing systems.
MIT License
Last Updated